Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood - HPLC
Simple handling
Cost effectiveness achieved as a result of optimised kit assembly
CE-IVD validated product ready for IVDR within timeframes and transition periods specified by the IVDR 2017/746

Vitamin B6 (PLP, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate)
Clinical relevance
Vitamin B6 comprises pyridoxine, pyridoxamine and pyridoxal, as well as their phosphate derivatives. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) is the active coenzyme form of vitamin B6, and is involved in nearly a hundred different enzymatic reactions. These include synthesizing and degrading amino acids, metabolising amino acids to carbohydrates and metabolising fatty acids. Vitamin B6 is also essential for the transmission of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, as well as for the biosynthesis of certain porphyrins. The quantity of consumed proteins is one of the things that the need for vitamin B6 is dependent on.
Vitamin B6 is available in many different foods, making vitamin B6 deficiency rare. Very unbalanced nutrition can still lead to a deficiency together with other water-soluble vitamins. This can cause a number of symptoms, including growth disorders, anaemia as a result of haem synthesis disturbances, chronic inflammation of the tongue and dermatitis. Many different metabolic disorders are also caused by a vitamin B6 deficiency, such as hyperhomocysteinemia.
An overdose from natural foods is nearly impossible as a matter of practicality, and is therefore only a result of excessive supplementation. It causes photosensitivity and certain neuropathies. Tachycardia and peripheral circulatory disorders have also been described in infants.
Product advantages
- Simple handling
- Cost effectiveness achieved as a result of optimised kit assembly
- Method for determination in plasma/serum also available (31000/S)
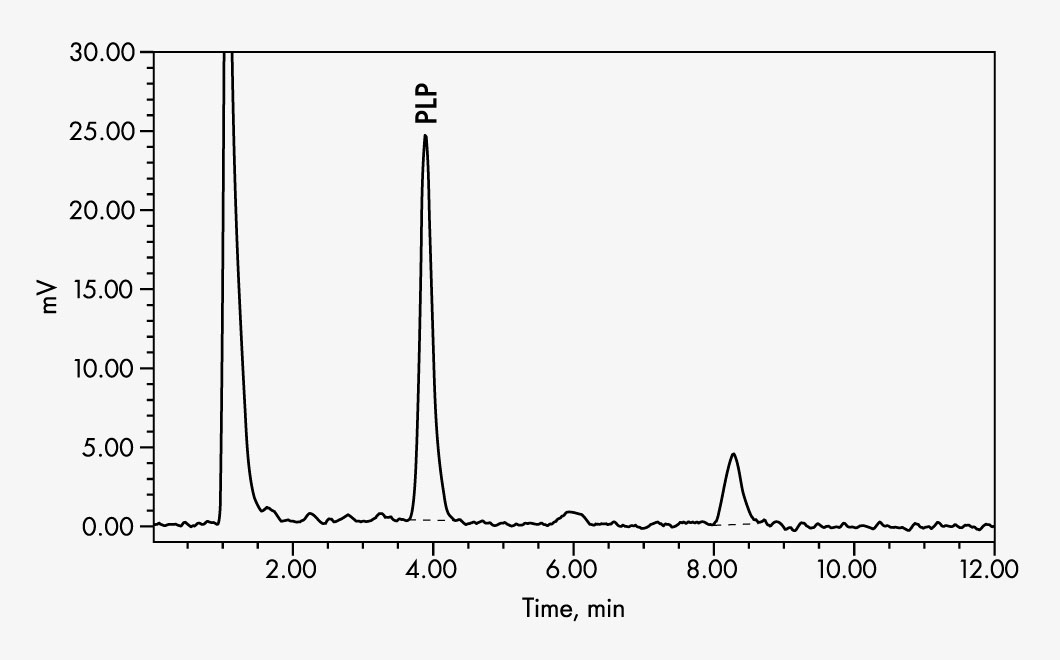
PLP can be simply and reliably determined from whole-blood samples by using this reagent kit for HPLC. Sample preparation starts with an effective protein precipitation step to release the analyte from its proteinous holoenzyme. Subsequent derivatisation produces a fluorescent PLP derivative. The chromatographic measurement is run on an isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector.
Chromsystems also offers additional methods using HPLC and UHPLC to achieve combined analysis of vitamin B6 with vitamin B1.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 0.6 µg/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 250 µg/l |
| Intraassay | CV < 1.3 % |
| Interassay | CV < 3.7 % |
| Recovery | 86 % |
| Specimen | Whole Blood |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | < 8 min |
| Injection Volume | 25 - 50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1 - 1.2 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Gradient | Isocratic |
| Wavelength | EX 320 nm |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of vitamin B6 every isocratic system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Vitamin B6 (PLP, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate) |
-
 DetailsOut of stock
DetailsOut of stock
-
 HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100
HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma - HPLC
-
 HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100
HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma - HPLC


Vitamin B6 (PLP, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate)
Clinical relevance
Vitamin B6 comprises pyridoxine, pyridoxamine and pyridoxal, as well as their phosphate derivatives. Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP) is the active coenzyme form of vitamin B6, and is involved in nearly a hundred different enzymatic reactions. These include synthesizing and degrading amino acids, metabolising amino acids to carbohydrates and metabolising fatty acids. Vitamin B6 is also essential for the transmission of neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, as well as for the biosynthesis of certain porphyrins. The quantity of consumed proteins is one of the things that the need for vitamin B6 is dependent on.
Vitamin B6 is available in many different foods, making vitamin B6 deficiency rare. Very unbalanced nutrition can still lead to a deficiency together with other water-soluble vitamins. This can cause a number of symptoms, including growth disorders, anaemia as a result of haem synthesis disturbances, chronic inflammation of the tongue and dermatitis. Many different metabolic disorders are also caused by a vitamin B6 deficiency, such as hyperhomocysteinemia.
An overdose from natural foods is nearly impossible as a matter of practicality, and is therefore only a result of excessive supplementation. It causes photosensitivity and certain neuropathies. Tachycardia and peripheral circulatory disorders have also been described in infants.
Product advantages
- Simple handling
- Cost effectiveness achieved as a result of optimised kit assembly
- Method for determination in plasma/serum also available (31000/S)
PLP can be simply and reliably determined from whole-blood samples by using this reagent kit for HPLC. Sample preparation starts with an effective protein precipitation step to release the analyte from its proteinous holoenzyme. Subsequent derivatisation produces a fluorescent PLP derivative. The chromatographic measurement is run on an isocratic HPLC system with fluorescence detector.
Chromsystems also offers additional methods using HPLC and UHPLC to achieve combined analysis of vitamin B6 with vitamin B1.
| Method of Analysis | HPLC |
|---|---|
| Number of Tests | 100 |
| Please note | The freely available information on this website, in particular on the sample preparation, are not sufficient to work with our products. Please read instructions and warning notices on products and/or instruction manuals. |
| Lower Limit of Quantitation | 0.6 µg/l |
| Upper Limit of Quantification | up to 250 µg/l |
| Intraassay | CV < 1.3 % |
| Interassay | CV < 3.7 % |
| Recovery | 86 % |
| Specimen | Whole Blood |
| Sample Preparation |
|
| Run Time | < 8 min |
| Injection Volume | 25 - 50 µl |
| Flow Rate | 1 - 1.2 ml/min |
| Column Temperature | ambient (~25 °C) |
| Gradient | Isocratic |
| Wavelength | EX 320 nm |
| Additional Info | For the HPLC analysis of vitamin B6 every isocratic system with fluorescence detector is suitable. |
| Parameters | Vitamin B6 (PLP, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate) |
-
 DetailsOut of stock
DetailsOut of stock
-
 HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100
HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma - HPLC
-
 HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100
HPLC Column Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/PlasmaOrder no.: 31100Vitamin B6 in Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma - HPLC